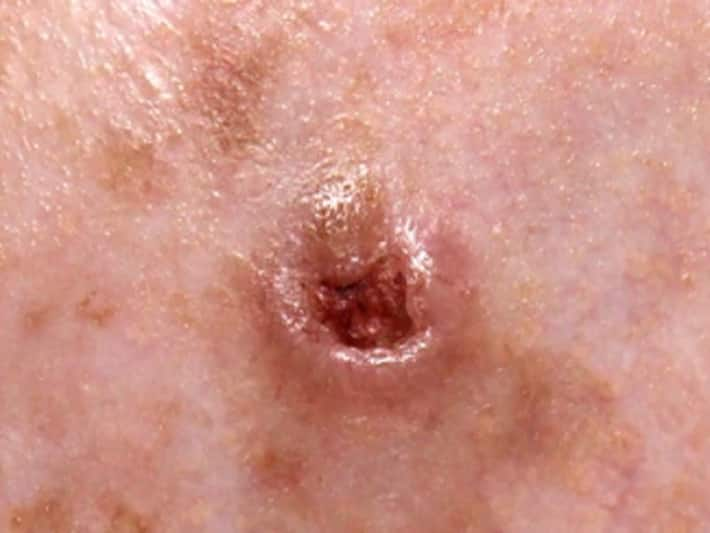
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC), the most common form of skin cancer, forms in the lowest layer of the epidermis of skin. The cancer rarely spreads (metastasize). But it can invade the surrounding tissues and cause significant damage and disfigurement.
Causes
The main cause is long term exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Genetics and light-coloured skin are the risk factors. Indoor tanning beds can also significantly increase chances of cancer. People with basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome) are prone to developing BCC.
Symptoms
The cancer appears as red patches, open sores, scar tissue or shiny, pearly nodules. Though it does not metastasize, it can grow and infiltrate vital structures around it and cause disfigurement.
Diagnosis
A biopsy is the only way to diagnose the condition
When a patient visits a doctor, he/she will first do a physical examination of the skin and then suggest a biopsy based on his/her suspicions. The doctor takes a small sample of the abnormal area or removes the whole abnormal area. Then a pathologist examines the skin cells under a microscope to check for cancer.
Different types of biopsy procedures are: Incisional biopsy – only a sample of tissue is removed; Excisional biopsy – an entire lump or suspicious lesion area is removed; Needle aspiration biopsy – a needle is used to remove a sample of tissue or fluid. In core needle biopsy a needle with a special tip is used. When a thin needle is used, the procedure is called a fine-needle aspiration biopsy.
Treatment
The treatment options commonly used to treat basal cell carcinoma are -
Medications: 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod cream are used for the treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma.
Surgery: Deeper cancers are surgically excised. Mohs surgery is an effective technique to treat basal cell carcinomas.
Radiotherapy: Radiotherapy uses ionizing radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumours. It is administered either externally through a machine (external beam radiotherapy) or internally by placing radioactive material in the body near tumour cells (brachytherapy).
Photodynamic therapy: Photodynamic therapy kills cancer cells. For this therapy, a doctor uses a special cream and a special light to treat the skin cancer.
Targeted therapy: Targeted molecular therapy with drug Dz13 has also been found to be effective against the cancer.
Prevention
Here are few tips to prevent basal cell carcinoma -





0 Comments