Central line insertion should be real-time ultrasound guided. The internal jugular is usually preferred to subclavian approach where possible as it is less likely to lead to pneumothorax
Indications for central line (central venous catheter) insertion- Administration of medications that require central access e.g. amiodarone, inotropes, high concentration electrolytes
- Fluid balance monitoring with CVP
- Intravenous access (long term or difficult peripherally)
Complications of central line (central venous catheter) insertion- Haemothorax
- Pneumothorax
- Haematoma
- Inadvertent arterial puncture
|
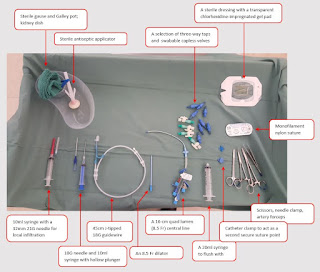
Equipment required for central line (central venous catheter) insertion- Ultrasound and sterile ultrasound sheath
- Sterile trolley
- Sterile field, gloves, gown and mask
- Seldinger central line kit
- Saline flush
- Chlorhexidine
- Lignocaine (4ml (2 vials) of 2% is reasonable)
- Suture
- Scalpel
- Sterile dressing
- Pressure bag to attach to monitoring
|
Contraindications to central line (central venous catheter) insertion- Coagulopathy
- Local infection
- Avoid in raised intracranial pressure- aim for a femoral approach if required
- Patient non-compliance
|
Pre-procedure- Consent patient if conscious otherwise document why the procedure is in the patients best interests
- Consent should include:
- Infection, bleeding (arterial puncture, haematoma, haemothorax), pain, failure, damage to surrounding structres (including pneumothorax), thrombosis.
- Set up sterile trolley
- Position patient with head down if they can tolerate it, with head facing away from side of insertion
- This ensures maximum venous filling
- Ultrasound area to define anatomy
- Having a nurse or assistant is helpful
|
Procedure for central line (central venous catheter) insertion- Wash hands and don sterile gown and gloves
- Clean the area and apply sterile field. Make sure to have some spare gauze swabs ready.
- Apply sterile sheath to the ultrasound probe
- Confirm anatomy
- Under ultrasound guidance insert lignocaine cutaneously, subcutaneously and around internal jugular.
- Whilst lignocaine has time to work flush all lumens of the line and then clamp all lumens except the Seldinger port
- Ensure caps are available for the lumens
- Under ultrasound guidance take Seldinger needle attached to syringe and insert into the internal jugular vein
- When blood is freely aspirated remove syringe and immediately inset Seldinger wire. This should pass easily
- Keeping hold of the inserted wire, remove the needle. Ensure the wire stays in the vein as you do this
- Use scalpel to make an small incision in the skin (approx 3mm). This should be done cutting away from the wire so as not to damage it
- Pass the dilator over the wire and gently but firmly dilate a tract through to the internal jugular.
- At this stage there may be some bleeding so ensure to have some swabs ready
- Remove the dilator and pass the central line over the Seldinger wire. Do not advance the line until you have hold of the end of the wire
- Once the central line is in place, remove the wire
- Aspirate and flush all lumens and re clamp and apply lumen caps
- Suture the line to allow 4 points of fixation
- Dress with a clear dressing so the insertion point can be clearly seen
|






0 Comments